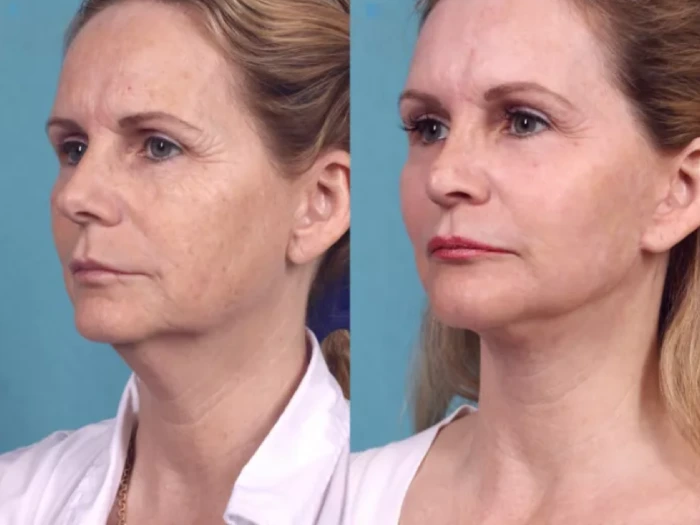
Hyperpigmentation causes dark patches on the skin that can affect confidence and appearance. Effective treatment depends on the type and severity of pigmentation, but a combination of topical products and professional procedures often yields the best results.
The best treatment for hyperpigmentation typically involves using targeted serums with ingredients like vitamin C, hydroquinone, or retinoids, combined with professional options like chemical peels or laser therapy to address deeper pigmentation. Consistency and sun protection are essential throughout any treatment plan to prevent further darkening.
Many over-the-counter products can help, but consulting a dermatologist ensures a personalized approach based on skin type and pigmentation cause. This article explores both at-home and clinical treatment options for achieving clearer, more even skin tone.
Top Hyperpigmentation Treatments
Effective treatments for hyperpigmentation target the skin’s pigment production and promote cell turnover. These approaches vary from topical applications to advanced professional therapies, each suited for different levels and types of pigmentation.
Topical Ingredients and Creams
Topical treatments commonly include ingredients like hydroquinone, retinoids, vitamin C, and azelaic acid. Hydroquinone is a strong pigment-inhibiting agent often prescribed in concentrations up to 4%. Retinoids accelerate skin cell turnover, helping to fade dark spots over time.
Vitamin C acts as an antioxidant and indirectly inhibits melanin production, making it a good option for mild hyperpigmentation. Azelaic acid is effective for both acne-related scars and melasma, and it suits sensitive skin.
Over-the-counter creams may combine these ingredients, but higher concentrations usually require a dermatologist’s prescription. Consistent use, typically over several weeks, is necessary to see improvement.
Professional In-Office Procedures
In-office treatments include chemical peels and microneedling, which promote exfoliation and stimulate collagen production. Chemical peels use acids like glycolic, lactic, or trichloroacetic acid to remove damaged skin layers and reduce pigmentation.
Microneedling creates controlled skin injuries to trigger healing, improving texture and dispersing pigment clusters. Some newer options, like the Rexonage3 treatment, utilize high-frequency currents to target pigmentation with no downtime.
These professional options often deliver faster and more significant results but carry risks such as irritation or pigment changes, especially in darker skin tones. A dermatologist’s evaluation is crucial before proceeding.
Laser and Light Therapies
Laser treatments target melanin with concentrated light beams to break down pigment. Common lasers include Q-switched, fractional, and pigment-specific types, each suited for different pigmentation types.
Intense Pulsed Light (IPL) therapy offers a broader light spectrum to address pigmentation and vascular discoloration simultaneously. These methods require multiple sessions and can cause temporary redness or swelling.
Lasers must be chosen carefully to avoid worsening hyperpigmentation, especially in darker skin. Professional expertise is essential to tailor the right wavelength and intensity for safe and effective outcomes.
How to Choose the Best Treatment for Hyperpigmentation
Selecting an effective treatment involves understanding the specific cause of the dark spots, evaluating the safety profile of each option, and considering how results will hold up over time. Tailoring the approach to skin type and lifestyle also plays a crucial role in success.
Identifying the Underlying Cause
Determining the root cause of hyperpigmentation is essential for choosing the right treatment. Common causes include sun damage, post-inflammatory responses, melasma, and hormonal changes. Each type may require different approaches.
A thorough examination by a dermatologist can help identify whether the pigmentation is superficial or deeper in the skin. This assessment may involve medical history review and, in some cases, diagnostic tests.
Treatments like chemical peels or topical agents such as hydroquinone work best on superficial pigmentation. Deeper or hormonal types might respond better to laser therapies combined with topical treatments.
Safety Considerations and Side Effects
Safety varies by treatment method and individual skin type. Some options, like over-the-counter creams containing vitamin C or niacinamide, generally carry low risk for side effects.
More aggressive treatments, including chemical peels or laser therapy, may cause redness, irritation, or post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation, especially in darker skin tones. These risks must be weighed carefully.
It is important to conduct patch tests and follow medical advice closely. Using sunscreen daily also minimizes the risk of worsening pigmentation during and after treatment.
Long-Term Results and Maintenance
Many hyperpigmentation treatments require ongoing maintenance to preserve results. For example, topical agents often need continuous application to prevent recurrence.
Procedures like laser toning or chemical peels may provide faster improvement but usually require repeat sessions spaced weeks or months apart.
Sun protection remains the cornerstone of long-term success. Without diligent use of broad-spectrum sunscreen, pigmentation may return despite treatment.
Consistency in skincare routines and periodic dermatologist consultations help ensure lasting, even-toned skin.